Silicone Pads for Keloids
Silicone Pads for Keloids: A Comprehensive Medical Treatment Guide
Silicone gel sheets and pads represent the gold standard, first-line treatment for keloid scars, offering a non-invasive approach to managing these challenging skin conditions. Current research demonstrates that silicone-based therapies can significantly reduce keloid thickness, improve coloration, and provide symptomatic relief for itching and pain, with effectiveness rates ranging from 70-82% for various types of keloid scars.

Medical-grade silicone scar sheets for reducing keloids and other scars, recommended for use over several weeks.
Understanding Keloids and Silicone Therapy
What Are Keloids?
Keloids are raised, thickened scars that extend beyond the original wound boundaries and tend to persist or worsen over time. Unlike normal scars or hypertrophic scars that remain within the original injury site, keloids result from excessive collagen production during the wound healing process, creating firm, often painful, and cosmetically concerning growths. These scars are more common in individuals with darker skin tones and those with genetic predisposition to abnormal scarring.
Silicone Gel Sheets: Medical-Grade Treatment
Silicone gel sheeting consists of medical-grade silicone polymers reinforced with a silicone membrane backing, creating a soft, semi-occlusive sheet that adheres to the skin. First discovered as a scar treatment in the 1980s in Australia, silicone therapy has evolved into the internationally recommended first-line treatment for pathological scarring. The sheets are designed to create a protective barrier over the scar while maintaining optimal hydration and healing conditions.
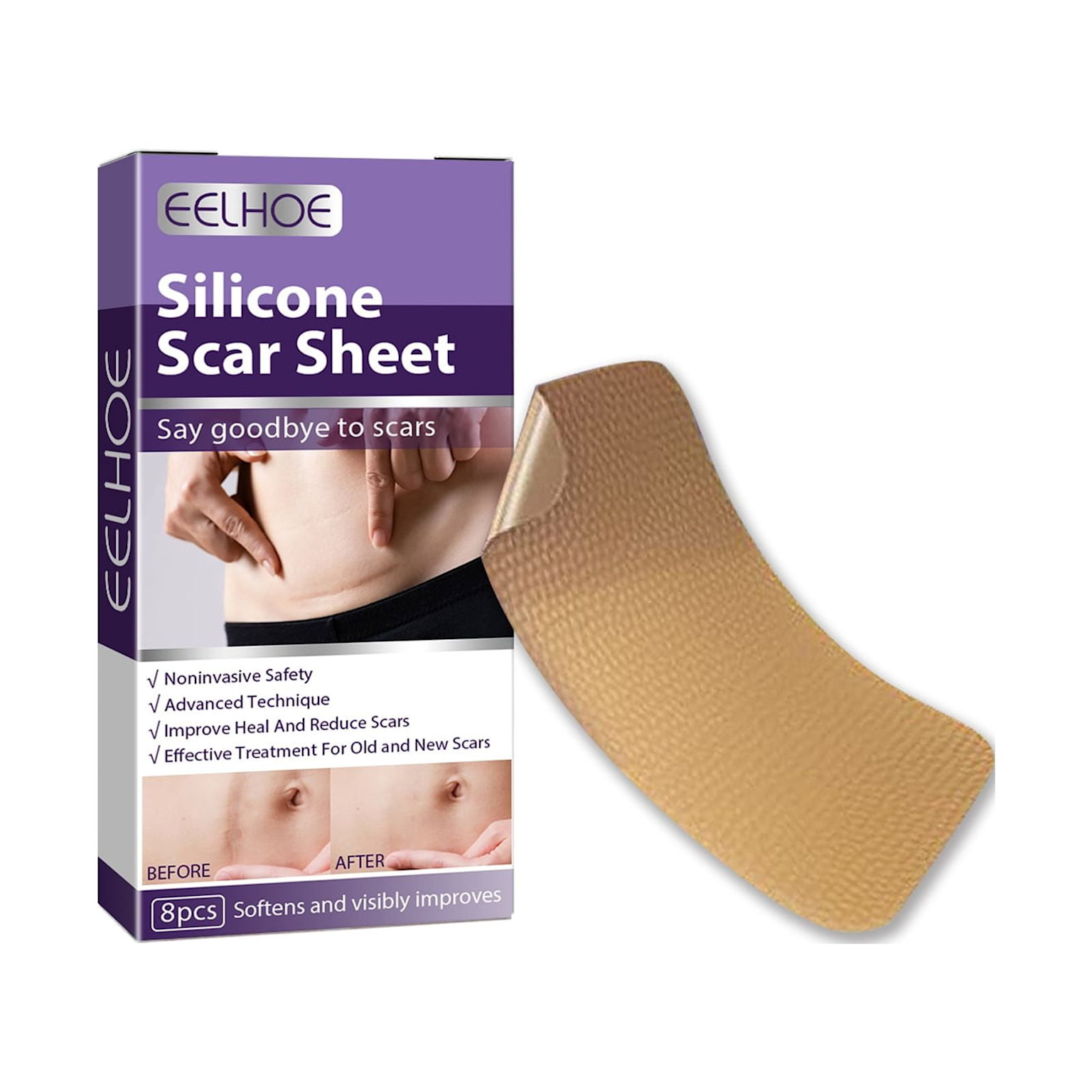
EELHOE silicone scar sheet with before and after results for scar treatment including keloids
Mechanism of Action and Scientific Evidence
How Silicone Works on Keloids
While the exact mechanism remains partially understood, research indicates that silicone gel sheeting works through multiple pathways. The primary mechanism involves occlusion and hydration of the scar tissue, which creates an optimal healing environment that normalizes collagen synthesis cycles. Studies suggest that hydration of the stratum corneum influences cytokine production and regulation, though specific factors affected by silicone treatment have not been fully determined.
The silicone creates a protective barrier that prevents chemical, physical, and microbial invasion of the scar site while maintaining appropriate moisture levels. This environment allows scars to mature through normalized collagen production, reducing the excessive collagen accumulation characteristic of keloids. Additionally, silicone sheets provide gentle pressure that may help flatten raised tissue and reduce symptoms like itching and discomfort.
Clinical Evidence and Effectiveness
Multiple systematic reviews and clinical trials support silicone therapy's effectiveness for keloid treatment. A major multicenter study involving 111 patients demonstrated that dermatologists scored silicone gel effectiveness as 82.3% good to very good for minor keloids and 70% good for major keloids. The study showed improvement across all key parameters including redness, hardness, elevation, and itchiness within three months of treatment.
A comprehensive 2013 Cochrane review of 20 trials involving 873 people found that silicone gel sheeting produced statistically significant reductions in scar thickness (mean difference -2.00) and significant color amelioration. However, reviewers noted that while evidence supports benefits, many studies were of poor quality and highly susceptible to bias.
Recent research published in 2023 confirms that silicone gel sheeting is considered an optimal treatment option for keloid scars, though high-quality randomized controlled trials remain limited. Current literature supports silicone therapy as first-line treatment particularly when combined with other interventions.
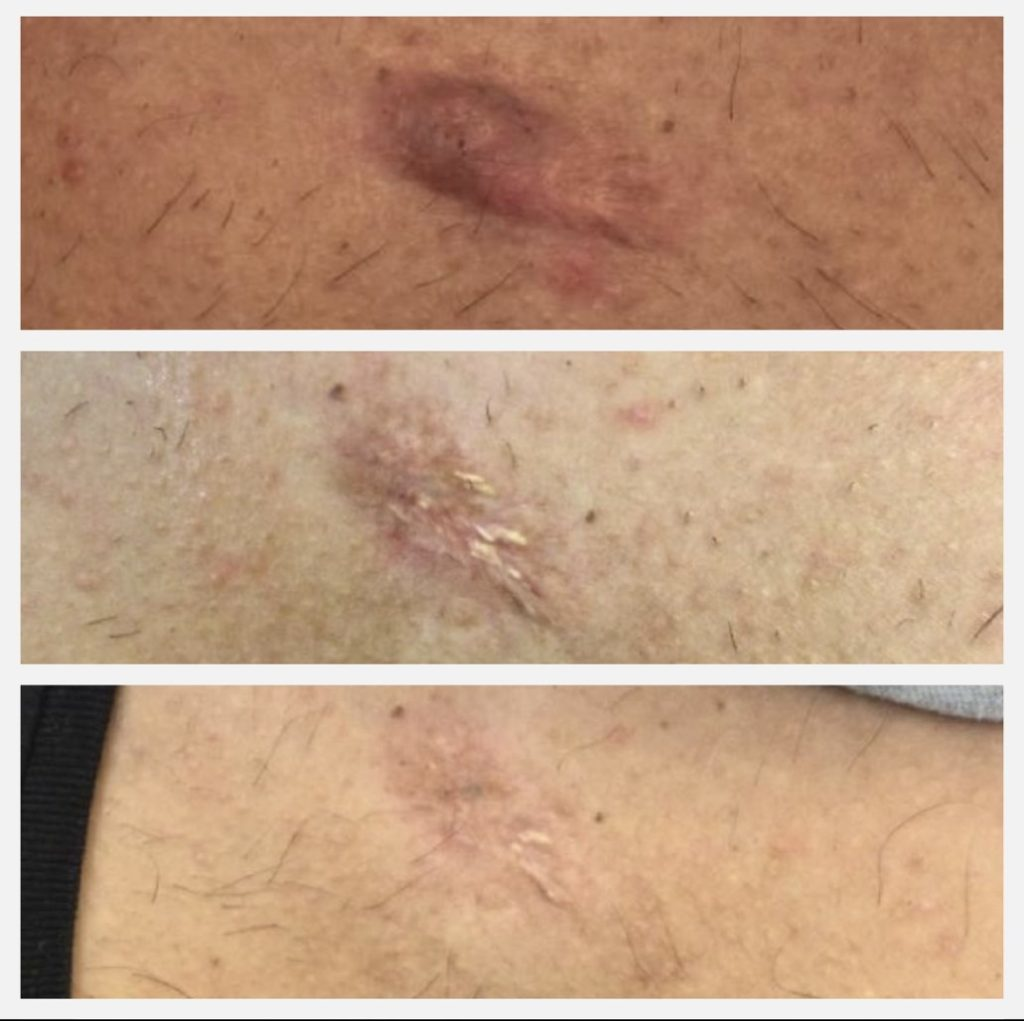
Progressive reduction of keloid scars on skin, showing before and after treatment results.
Treatment Application and Guidelines
Who Should Use Silicone Therapy
Silicone gel sheets are recommended for several patient groups:
- High-risk individuals: Those with a history of hypertrophic or keloid scarring
- Post-surgical patients: Beginning treatment when full re-epithelialization occurs (approximately 2 weeks after wound closure)
- Patients with immature scars: Red, thickened scars causing symptoms like itchiness and pain
-
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2989813/
Pediatric patients: Excellent option for children who cannot tolerate intralesional steroid injections - Individuals seeking non-invasive treatment: Those preferring to avoid injections or surgery
Application Instructions

Instructions for using Elastoplast silicone scar patches to reduce new and old scars.
Proper application is crucial for treatment success:
- Preparation: Ensure the affected area is completely clean and dry. Remove any excess creams or moisturizers
- Initial Application: Remove protective backing and place the adhesive side directly onto the scar, ensuring the silicone sheet covers an area 2cm around the scar
- Gradual Introduction: Build skin tolerance gradually:
- Days 1-2: Wear for 4 hours - Days 3-4: Increase to 8 hours - Continue increasing by 2-hour increments daily until reaching minimum 12 hours
-
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2989813/
Optimal Duration: Wear for 12-24 hours daily, with 12 hours being the minimum effective duration. Maximum benefit requires consistent use for 2-3 months minimum - Daily Maintenance: Clean the silicone sheet twice daily with mild soap and rinse thoroughly. Pat dry with a non-fluffy towel
Treatment Duration and Expectations
The recommended treatment duration varies based on scar age and type:
- New scars: Minimum 60-90 days of consistent use
- Mature scars: 4-6 months or longer if improvement continues
- Established keloids: May require 3-12 months for noticeable results
Clinical improvements typically begin within 2-3 weeks, with texture improvements appearing first, followed by pigmentation changes, then height reduction. Each silicone sheet can be reused for 4-8 weeks depending on care and wearing time.
Product Types and Brand Options
Available Formulations
Silicone Gel Sheets: Reusable, thick sheets lasting 4-8 weeks:
- Biodermis: Medical-grade, highly rated (4.8/5), effective for all scar types
- ScarAway: Affordable option, good adhesion, effective for keloids
- Cica-Care: Clear, thick sheets lasting approximately 4 weeks
- Mederma: Includes UPF 50 protection, breathable formulation
- Kelo-cote sheets: Recommended specifically for keloids
Silicone Gel: Self-drying liquid formulation:
- Kelo-cote gel: Forms invisible, waterproof layer within minutes
- Applied twice daily, dries in 3-5 minutes
- Compatible with makeup and sunscreen after drying
- More convenient for irregular or large scars
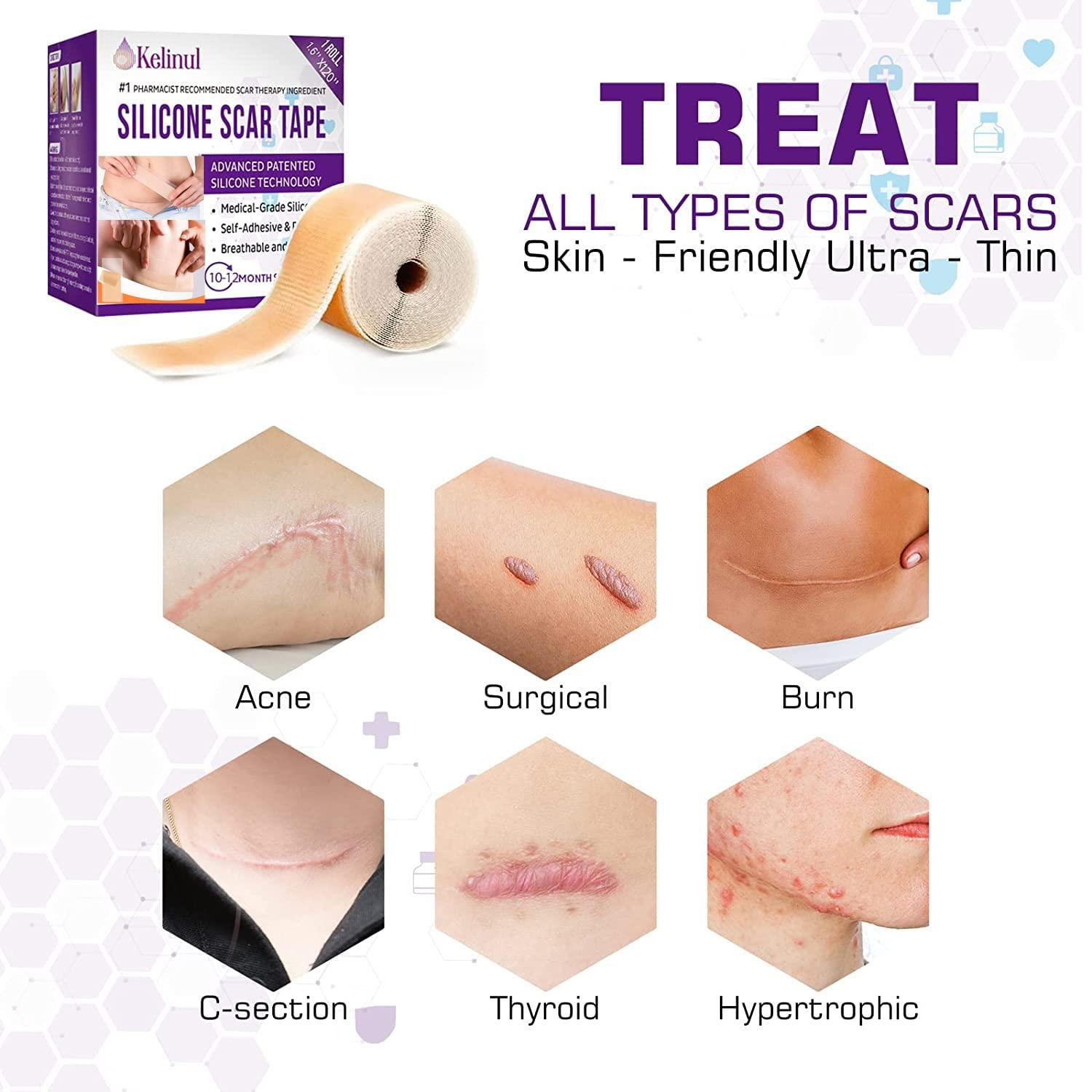
Kelinux silicone scar tape for treating various types of scars including acne, surgical, burn, C-section, thyroid, and hypertrophic scars.
Cost Considerations
Treatment costs vary significantly across the UK:
- Silicone sheets: £20-60 per pack (lasting 1-2 months)
- Silicone gels: £25-45 per tube (2-3 month supply)
- NHS availability: Limited coverage; GP referral may be required for prescription
- Private treatment: More readily available but at higher cost
- Long-term investment: Total treatment cost typically £100-300 over 3-6 months
Safety Profile and Side Effects
Common Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, silicone therapy can cause several side effects, particularly in hot climates:
Skin-related reactions:
- Persistent itching (reported in 80% of users in hot climates)
- Skin rash (28% of users)
- Contact dermatitis (rare but possible)
- Skin maceration from prolonged moisture exposure (16% of users)
- Allergic reactions causing redness and swelling
Product-related issues:
- Adhesive residue causing irritation
- Poor durability in hot, humid conditions
- Foul odor development (4% of users)
- Poor adhesion on oily skin
Serious but rare complications:
- Folliculitis from hair follicle occlusion
- Skin breakdown (8% of users)
- Hyperpigmentation, particularly in darker skin tones
- Extended healing periods from improper application
Precautions and Contraindications
Silicone therapy should be avoided in certain situations:
- Open wounds or unhealed skin: Never apply to scabs or broken skin
- Active skin conditions: Avoid use on dermatological conditions disrupting skin integrity
- Known allergies: Patients with silicone sensitivity should avoid treatment
- Third-degree burns: Not appropriate for severe burn injuries
Safety recommendations:
- Perform patch test before regular use (wear for 2 hours initially)
- Monitor skin condition carefully during treatment
- Discontinue if severe irritation occurs
- Maintain proper hygiene with daily cleaning
- Avoid talcum powder use with silicone products
Treatment Effectiveness and Limitations
Success Rates by Keloid Type
Clinical studies demonstrate varying effectiveness based on keloid characteristics:
- Minor keloids: 82.3% good to very good results
- Major keloids: 70% good results
- Hypertrophic scars: 80% good to very good outcomes
- Immature scars: 88.9% good to very good results (higher than mature scars at 75%)
Realistic expectations:
- Silicone rarely completely resolves keloids but significantly improves appearance
- Primary benefits include reduced thickness, improved color, and symptom relief
- Prevention of keloid worsening and recurrence after other treatments
- Enhanced patient quality of life through reduced itching and pain
Combination Therapy Approaches
Modern keloid treatment increasingly emphasizes combination approaches rather than monotherapy. Research demonstrates that combined treatments show superior outcomes compared to single interventions:
Effective combinations:
- Silicone sheets + corticosteroid injections (first-line recommendation)
- Silicone therapy + pressure garments
- Post-surgical silicone application + steroid injections
- Silicone treatment + laser therapy for established keloids
Treatment sequencing:
- Initial keloids: Silicone + compression therapy
- Growing keloids: Add intralesional corticosteroids after 4-6 weeks
- Resistant keloids: Consider surgical excision with post-operative silicone therapy
Comparison with Alternative Treatments
Silicone vs. Corticosteroid Injections
Silicone advantages:
- Non-invasive and painless application
- Suitable for pediatric patients
- Minimal side effects compared to steroid injections
- Can be used preventatively
- Lower risk of skin atrophy or dyspigmentation
Steroid injection advantages:
- Faster initial results (weeks vs. months)
- More effective for established, thick keloids
- Direct action on abnormal collagen production
- Lower time commitment for patients
Combined approach: Current guidelines recommend using both treatments together for optimal results, with silicone providing continuous treatment and steroids addressing acute inflammatory components.
Silicone vs. Surgical Options
Surgical removal alone shows poor outcomes with high recurrence rates (45-100%), leading to recommendations against excision as monotherapy. However, surgical excision combined with post-operative silicone therapy demonstrates significantly improved results:
Surgery + silicone benefits:
- Immediate cosmetic improvement from excision
- Silicone prevents recurrence during healing
- Lower regrowth rates compared to surgery alone
- Suitable for large or severely disfiguring keloids
Clinical Guidelines and Recommendations
International Treatment Protocols
A multidisciplinary international expert panel established practical guidelines for keloid management:
Primary treatment protocol:
- Initial approach: Silicone gel sheeting + compression therapy + moisturizing
- 4-6 weeks: If keloids continue growing, add intralesional corticosteroids
- After 12 months: Consider surgical excision with adjuvant therapy if no response
Prevention protocol: Begin silicone therapy within 2 weeks of wound closure for high-risk patients.
Patient Selection Criteria
Ideal candidates for silicone therapy:
- History of abnormal scarring
- Recent surgical procedures in high-risk individuals
- Immature keloids (red, raised, symptomatic)
- Patients seeking non-invasive treatment
- Children requiring gentle treatment options
- Post-operative keloid prevention
Less suitable candidates:
- Patients expecting rapid results (weeks rather than months)
- Those with active skin conditions or allergies
- Individuals unable to maintain consistent daily application
- Cases requiring immediate dramatic improvement
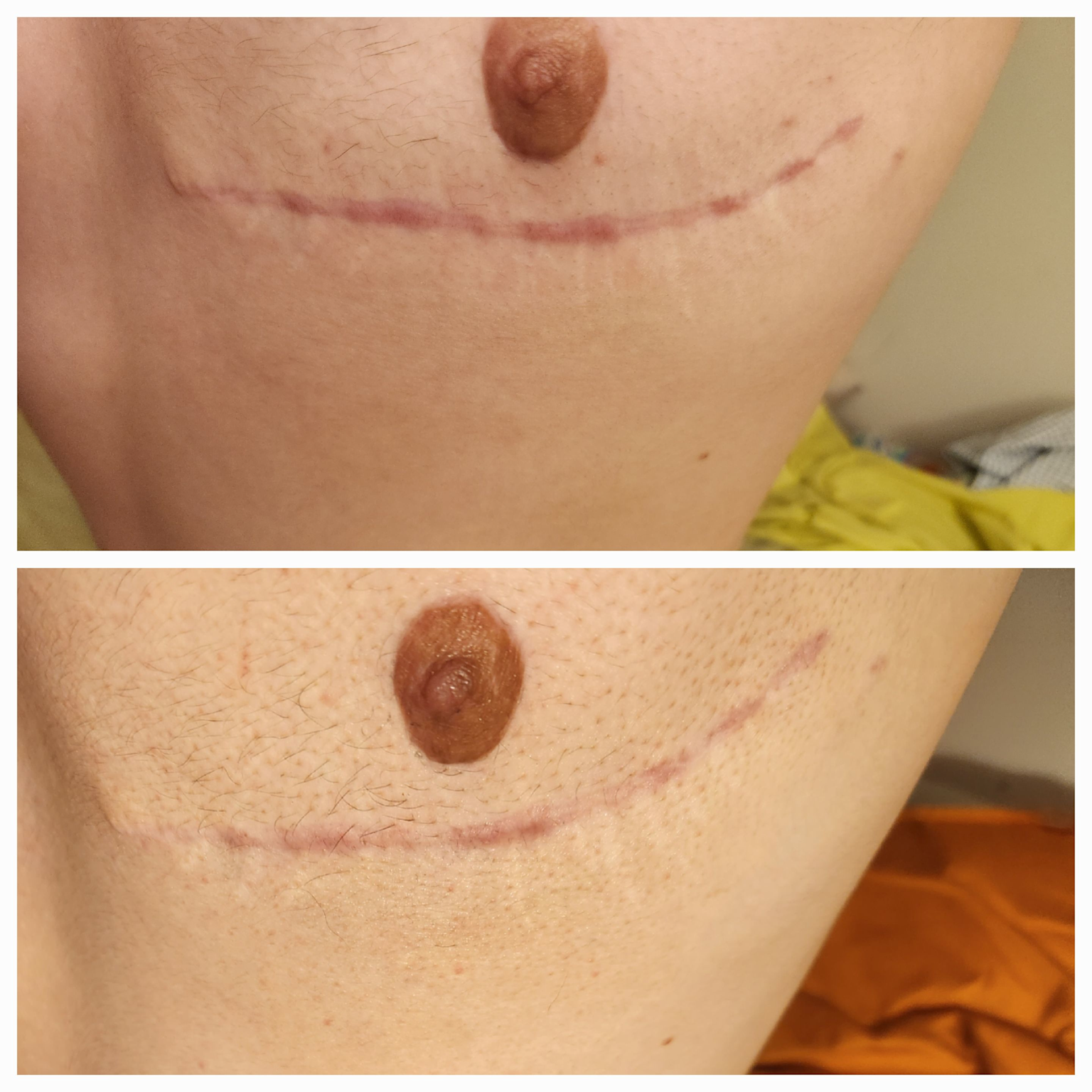
Comparison of a keloid scar before and after 1.5 months of silicone gel treatment showing reduced redness and raised texture.
Conclusion
Silicone gel sheets and pads represent the most evidence-based, non-invasive treatment option for keloid scars, with international medical consensus supporting their use as first-line therapy. While treatment requires patience and consistency over months rather than weeks, clinical evidence demonstrates significant improvements in scar thickness, coloration, and associated symptoms for 70-80% of patients.
The key to successful treatment lies in proper patient selection, correct application technique, and realistic expectations about treatment duration and outcomes. Modern keloid management increasingly emphasizes combination approaches, with silicone therapy serving as the foundation treatment enhanced by targeted interventions like corticosteroid injections when necessary.
For individuals with keloid scars, silicone therapy offers a safe, accessible treatment option that can significantly improve both the physical appearance and psychological impact of these challenging skin conditions. However, consultation with dermatology specialists remains essential for comprehensive treatment planning and monitoring, particularly for large, established, or treatment-resistant keloids.
Great post! Really enjoyed reading this.
ReplyDeleteRestore your skin’s smoothness and confidence with our medical-grade post-surgery scar treatment. Using advanced laser technology, regenerative serums, and dermatologist-designed protocols, 1Signature Clinic helps reduce scar thickness, redness, pigmentation, and texture irregularities safely and effectively. Ideal for C-section scars, surgical incisions, trauma scars and more for visibly smoother, healthier-looking skin. If you're interested, feel free to visit our website for more information: post surgery scar treatment